Anodizing Reference Guide
Anodizing is used to increase surface hardness, wear resistance and dielectric strength.
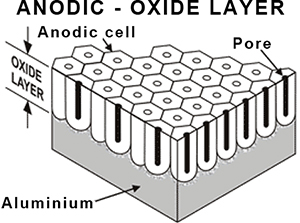
Anodizing can also provide a good base for painting or colouring, creating an extremely stable but porous oxide layer on the surface of aluminum.
Type Thickness
Type II
Conventional coatings produced 1.8μ-25.4μ
from sulfuric acid bath
Type I A
Conventional coatings produced 0.5μ-7.6μ (microns)
from chromic acid bath
Type I B
Low voltage chromic acid anodizing (20 volts) 0.5μ-7.6μ
Used for 7000 series alloys
Type III
Hard coat (uniform anodic coatings) 12.7μ-115μ
• Class 1
- Non dyed
• Class 2
- Dyed
Test Methods For Type II Anodized Aluminum
Oxide Coating Thickness
ASTM B 244-79
ASTM B 487-85 Min Thickness
Class I 18 Microns (μ)
Class II 10 Microns
Oxide Coating Weight and Apparent Density
ASTM B 137-89 Min Weight Min Density
Class I 4.18 mg/cm2 2.32 g/cm3
Class II 2.40 mg/cm2 2.32 g/cm3
(Adopted from AMAA 611)
Corrosion Resistance
ASTM B 117-90 Min Hours Max Spots
Class I 3000 15
Class II 1000 15
Seal Quality
ASTM B 136-77
ASTM B 680-80
ISO 3210 Max Weight Loss
Class I 40 mg/dm2
Class II 40 mg/dm2
Aluminum Alloy Reference for Anodizing
| Series (AA)* |
Alloying Constituants |
Metal Properties |
Coating Properties |
Uses | A.Q.** Types |
Non-A.Q.** Types |
| 1000 | None | soft, conductive | clear, bright | cans architectural |
none | 1100, 1175 |
Finishing advice: Care should be taken when racking this soft material;
good for bright coatings; susceptible to etch staining.
| 2000 | Copper |
very strong,hard, |
yellow, poor protection |
aircraft mechanical |
none | 2011, 2017 2219, 2224 |
Finishing advice: Since copper content is > 2%, these produce yellow, poor weather-resistant coatings; don't mix with other alloys on load
| 3000 | Manganese | strong, small grains |
grayish brown |
cans, architectural lighting |
none | 3003, 3004 |
Finishing advice: Difficult to match sheet-to-sheet (varying degrees of gray/brown); used extensively for lighting
| 4000 | Silicon | strong, fluid |
dark gray |
architectural, welding, wire |
none | 4043, 4343 |
Finishing advice: Produce heavy black smut which is hard to remove;
4043 & 4543 used for architectural dark gray finishes in past years
| 5000 | Magnesium | strong, ductile, fluid |
clear, good |
architectural, welding, wire, lighting |
5005, 5657 |
5052, 5252 |
Finishing advice: For 5005 – keep silicon < 0.1% and magnesium between 0.7%
and 0.9%; watch for oxide streaks; 5005 used extensively for architectural
| 6000 |
Magnesium &Silicon |
strong, ductile |
clear, good |
clear, good protection |
6063, 6463 |
6061, 6101 |
Finishing advice: Matte-iron > 0.2%; bright-iron < 0.1%;
6063 best match for 5005; 6463 best for chemical brightening
| 7000 |
Zinc |
very strong |
clear, good |
automotive | none | 7029, 7046, 7075 |
Finishing advice: Zinc over 5% will produce brown tinted coating;
watch zinc in effluent stream; good for bright coatings
** A.Q. - Anodizing Quality - material suitable for architectural anodizing applications
TYPE I “Chromic Acid”
Color will vary from clear to dark gray depending on alloy. Copper bearing alloys only
yield gray colors. Not as readily dyed as sulfuric anodize due to thinness of coating.
New salt spray requirement is 336 hours
(5% solution per method 811 or FED-STD-No. 151)
Type I Chromic acid anodized coating. This process is used principally for
the treatment of aircraft parts. An example is the Bengough-Stewart
process where a 30-50 g/l chromic acid bath is maintained at
100°F and the voltage is gradually raised to 50V. Adjustments
are made for high copper, zinc, and silicon alloys. Coating weights
must be greater than 200 mg/ft2. Criteria for corrosion resistance,
paint adhesion, and paint adhesion testing must be specified.
Type IB Low voltage (22)2V) chromic acid anodized coating. Typically associated
with higher temperature, more concentrated chromic acid electrolytes.
Coating weights must be greater than 200 mg/ft2. Criteria for corrosion
resistance, paint adhesion, and paint adhesion testing must be specified.
Type IC Anodized coating produced in a non-chromic acid electrolyte.
As with other Type I coating processes, the treatment is designed to
impart corrosion resistance, paint adhesion, and/or fatigue resistance
to an aluminum part. Coating weights must fall between 200-700 mg/ft2.
Criteria for corrosion resistance, paint adhesion, and paint adhesion
testing must be specified.
TYPE II “Sulfuric Acid”
| MECHANICAL FINISHING | A.A. | COMMON | DESCRIPTION | EXAMPLES OR FINISHING METHODS |
| As fabricated | M-10 | Unspecified | ||
| M-12 | Nonspecular as fabricated | No particular reflectiveness | ||
| Buffed | M-21 | Smooth specular | Polished first with coarser than 320 grit, followed by 320 grit, then buffed with Alum oxide | |
| M-22 | Specular | Buffed with Alum oxide compound | ||
| Directional textured | M-31 | Fine satin | Sanded with 320-400 grit Alum oxide | |
| M-32 | Medium satin | Sanded with 180-220 grit Alum oxide | ||
| M-33 | Coarse satin | Sanded with 80-100 grit Alum oxide | ||
| M-35 | Brushed | Brushed with stainless steel wire brush | ||
| CHEMICALFINISHING | ||||
| Nonetched Cleaning | C-11 | Degreased | Organic solvent treated | |
| C-12 | Inhibited chemical cleaned | Soap cleaner only | ||
| Etched | C-22 | R-1 | Medium matte | Sodium hydroxide (caustic soda) 30-45 gr/li @ 60-65˚C for 5 min |
| Brightened | C-31 | R-5 | Highly specular | Chemical bright dip solution of the proprietary phosphoric-nitric acid type, or electropolishing |
| C-32 | Diffuse bright | Etched finish C-22 followed by Brightened finish C-31 |
||
| ANODIC COATING | ||||
| General | A-11 | Prep for other applied coatings |
15% Sulfuric acid @ 20˚C, 12 amps/sq ft. for 10 min. sometimes not sealed |
|
| Decorative | A-21 | Clear coating 2.5μ-7.5μ | 15% Sulfuric acid @ 20˚C, 12 amps/sq ft. |
|
| A-211 | 200 | Clear coating min. 2.5μ | 15% Sulfuric acid @ 20˚C, 12 amps/sq ft. for 10 min. |
|
| A-212 | 201 | Clear coating min. 5μ | 15% Sulfuric acid @ 20˚C, 12 amps/sq ft. for 15 min. |
|
| A-213 | 202 | Clear coating min.7.5μ mil | 15% Sulfuric acid @ 20˚C, 12 amps/sq ft. for 20 min. |
|
| A-23 | Coating with impregnated color |
15% Sulfuric acid @ 20˚C, 12 amps/sq ft., followed by dyeing with organic or inorganic colors |
||
| A-24 | Coating electrolytically | 15% Sulfuric acid @ 20˚C, 12 amps/sq ft. , deposited color followed by deposition of inorganic metallic salts |
||
| Architectural Class 2 |
A-31 | 204 | Clear coating | 15% Sulfuric acid @ 20˚C, 12 amps/sq ft. |
| 10μ-18μ | A-33 | Coating with impregnated color |
15% Sulfuric acid @ 20˚C, 12 amps/sq ft. for 30 min., followed by dyeing with organic or inorganic colors. |
|
| A-34 | Coating electrolytically | 15% Sulfuric acid @ 20˚C, 12 amps/sq ft. deposited color for 30 min., followed by deposition of inorganic metallic salts. |
||
| Architectural Class 1 |
A-41 | 215 | Clear coating | 15% Sulfuric acid @ 20˚C, 12 amps/sq ft. |
| 18μ and more | A-43 | Coating with impregnated color |
15% Sulfuric acid @ 20˚C, 12 amps/sq ft. for 60 min., followed by dyeing with organic or inorganic colors. |
|
| A-44 | Coating electrolytically | 15% Sulfuric acid @ 20˚C, 12 amps/sq ft. deposited color for 60 min., followed by deposition of inorganic metallic salts. |
Data derived from “Designation System for Aluminum Finishes” (DAF45), published by The Aluminum Association
TYPE III “Hard Coating”
Color will vary from light tan to black depending on alloy and thickness. Color overtones
listed below may vary with the use of additives and/or the process. Can be dyed in darker
colors depending on thickness. Coating PENETRATES base metal as much as builds up
on the surface. The term THICKNESS includes both the buildup and penetration. Provides
very hard ceramic type coating. Abrasion resistance will vary with alloy and thickness of
coating. Good dielectric properties. Corrosion resistance is good, but recommend sealing in
5% dichromate solution where increased corrosion resistance is required. Where extreme
abrasion resistance is required do not seal as some softening is encountered.
Type III Anodize Thickness Guide
| Alloy | Major Constituent (in) | Maximum Thickness* | Color Overtones*** |
| 5005 | Magnesium | .0035 | Gray/Brown |
| 5052 | Magnesium | .0035 | Gray/Brown |
| 5083 | Magnesium | .0035 | Gray/Brown |
| 6061 | Mag/Silicon | .003 | Dark Gray |
| 6063 | Mag/Silicon | .004 | Green |
| 6105 | Mag/Silicon | .0035 | Gray/Green |
| 6262 | Mag/Silicon | .0025 | Gray |
| 6463 | Mag/Silicon | .003 | Gray |
| 7075 | Zinc | .004 | Bronze |
Case Studies
- Surface finishing
- Aluminum
Related Tags :